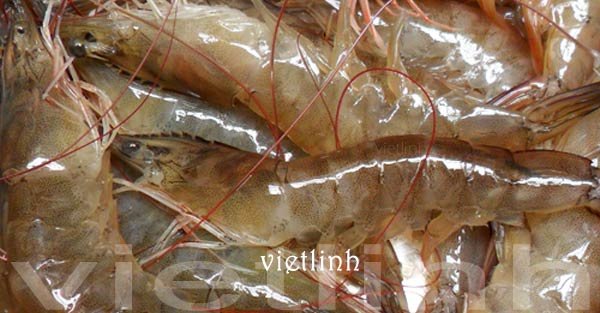
Soft shell disease in white leg shrimp
2.5. Some common diseases and their treatments
2.5.4. Soft shell disease in white leg shrimp
* Signs:
Commercial shrimp with soft shell disease often show these signs:
– Shrimp with dull color, soft or very soft shell, or shell not attached to meat.
– Shrimp with soft shell are often weak, inactive, vulnerable to diseases, and easily attacked by others; dead bodies spread everywhere.
– Shrimp with soft shells are usually growing slowly are susceptible to opportunistic diseases. The diseases usually occur in whiteleg shrimp ponds with intensive farming. Shrimp’s commercial value is reduced.
* Pathogens:
Soft shell disease in whiteleg shrimp relates to the environment and nutrition. Reasons: malnutrition, the lack of calcium and phosphorus in feed, low hardness.
– Water in pond is contaminated by pesticide.
– Low levels of phosphorus in the water.
* Preventions – treatments:
– Manage the environment with alkalinity from 80-160mg/l by using CaCO3 lime or dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) periodically once a week for the pond.
– Manage pond environment appropriately and stably; avoid shocks in shrimp.
– Add appropriate minerals in the diet, such as calcium/phos, Premix, etc.
Source: Temporary process for safe brackish-water shrimp farming in areas affected by diseases in Vietnam. According to The Official Dispatch No. 10/TCTS-NTTS. January 6th, 2015. Vietnamese Directorate of Fisheries
Viet Linh 2015. Translated by Sonia Linh V.